CO2 reduction
Atmospheric CO2 levels are steadying increasing due to human consumption of fossil fuels, resulting in climate changes and global warming. To mitigate atmospheric CO2 emission and its consequences, technologies able to produce substitute fuels via the reduction of CO2 molecules are actively sought after. Great efforts have been committed and outstanding results have been achieved, however giving electrons to stable CO2 molecules remains a very challenging task.
ABCforCO2 proposes to develop new organic catalysts for CO2 reduction into fuels or added-value chemicals. 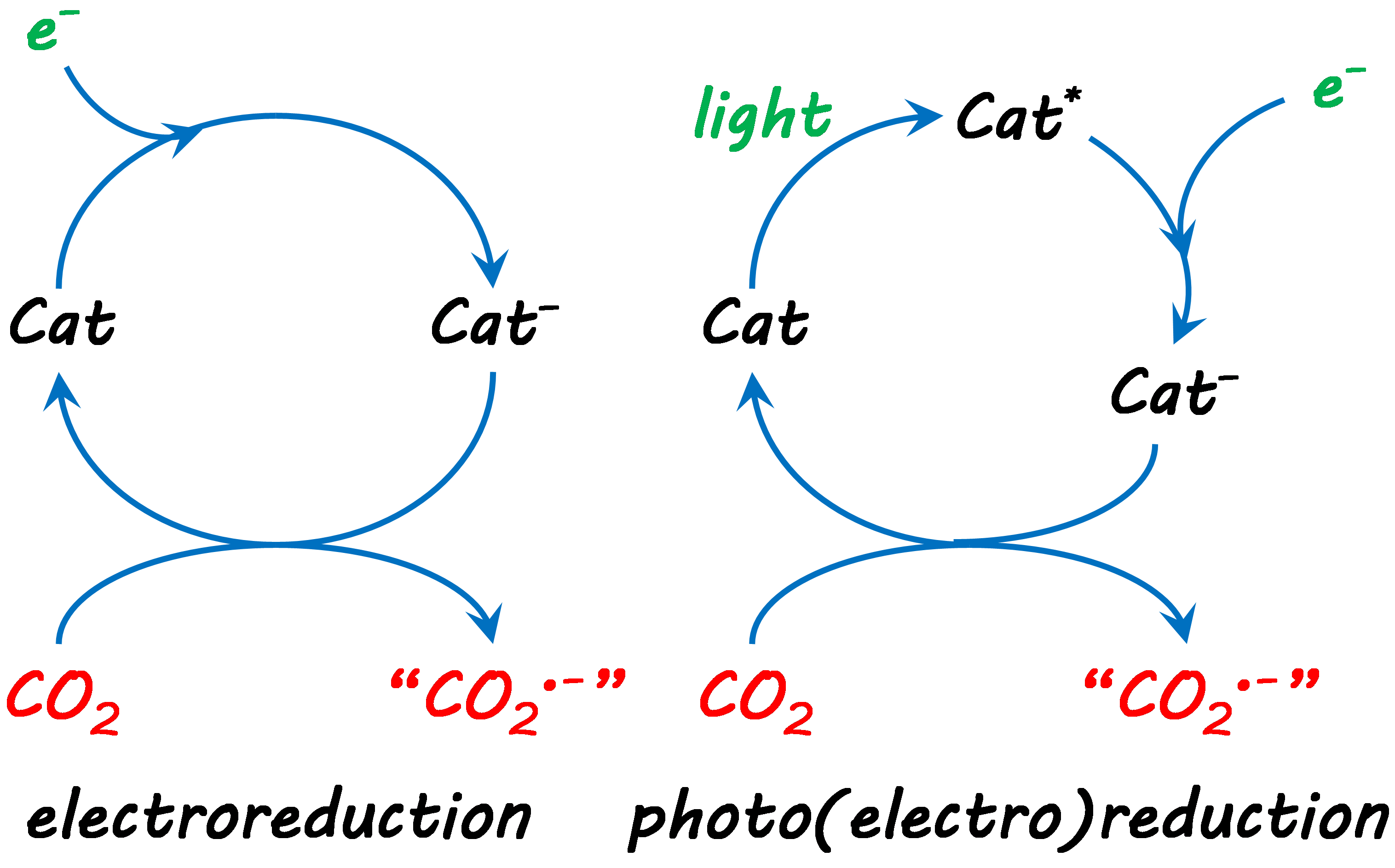 Such catalysts will be investigated in electroreduction processes, electricity being the electron source in these conditions. The intended catalysts being also photocatalysts, photoreduction and photoelectroreduction processes will be evaluated as well. The synthesis of the catalysts will be performed in the lab of Prof. Önder Metin (KU, Chemistry department) and the catalytic performances for CO2 reduction will be evaluated in the lab of Prof. Uğur Ünal (KU, Chemistry department).
Such catalysts will be investigated in electroreduction processes, electricity being the electron source in these conditions. The intended catalysts being also photocatalysts, photoreduction and photoelectroreduction processes will be evaluated as well. The synthesis of the catalysts will be performed in the lab of Prof. Önder Metin (KU, Chemistry department) and the catalytic performances for CO2 reduction will be evaluated in the lab of Prof. Uğur Ünal (KU, Chemistry department).
Cationic Helicenes and their applications
 Helicenes are inherently chiral ortho-condensed polyaromatics. Whereas neutral helicenes exhibit optical properties in the UV or blue part of the spectral window, their cationic analogues usually display absorption and emission at lower energy. Cationic [6]helicenes in particular are characterized by large configurational stabilities, conferring outstanding chiroptical properties to this class of derivatives with large dissymmetry factors in Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) and Circularly Polarized Luminescence (CPL). Such compounds can find applications in analytics, biochemistry, catalysis and synthesis, physics and surface sciences.
Helicenes are inherently chiral ortho-condensed polyaromatics. Whereas neutral helicenes exhibit optical properties in the UV or blue part of the spectral window, their cationic analogues usually display absorption and emission at lower energy. Cationic [6]helicenes in particular are characterized by large configurational stabilities, conferring outstanding chiroptical properties to this class of derivatives with large dissymmetry factors in Electronic Circular Dichroism (ECD) and Circularly Polarized Luminescence (CPL). Such compounds can find applications in analytics, biochemistry, catalysis and synthesis, physics and surface sciences.

