Kadir Mert Okumuş
Çağlar Can Tüz

1.1. Aim
In the card dispenser project, our main objectives include improving proficiency in 3D designing, learning and experiencing manufacturing processes, and understanding of a systems dynamic properties, such as being able to create a governing equation for a dynamic system, and both theoretically calculating and experimentally observing magnıtudes of position, velocity, and acceleration vectors.
1.2. Card Dispenser Mechanism
Card Dispenser Mechanisms are supplied for card vending applications in various self service industries and are mostly used in automats. This automation system might be used on a bigger scale in factorization (e.g. pushing metal plates that are stacked onto a conveyor belt.)
1.1. Aim
In the card dispenser project, our main objectives include improving proficiency in 3D designing, learning and experiencing manufacturing processes, and understanding of a systems dynamic properties, such as being able to create a governing equation for a dynamic system, and both theoretically calculating and experimentally observing magnıtudes of position, velocity, and acceleration vectors.
1.2. Card Dispenser Mechanism
Card Dispenser Mechanisms are supplied for card vending applications in various self service industries and are mostly used in automats. This automation system might be used on a bigger scale in factorization (e.g. pushing metal plates that are stacked onto a conveyor belt.)
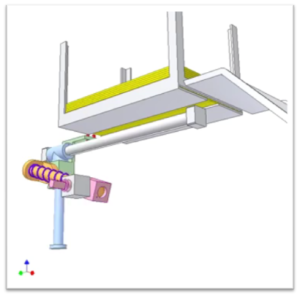
Design of Card Dispenser Mechanism
The design process has begun by collecting information from the YouTube link [2] provided on our proposal sheet. After analyzing the video, we have begun by rough estimations for measurements of parts and analysis of dynamics between those parts. For the first design we come up with size that is able hold A4 paper. However, main challenge was the finding the ideal size for the moving parts which is changes continuous rotational motion into rectangular and linear motions.
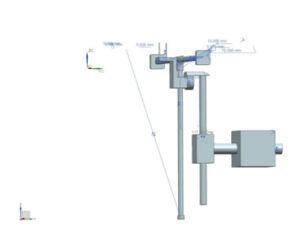
Using CAD Software NX we were able to draw a 3D model of all parts, which were then assembled in virtual environment.
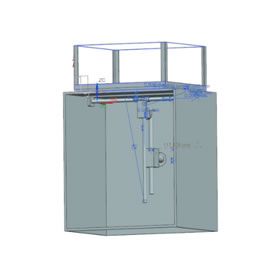
The fluidity of motion and the dynamics between the drawn parts was tested in the program first. Because we were going to use a laser cutting machine to cut our parts out of plexiglass, our first design was later tweaked to ease the producing process and thus we produced more prism parts which were put together with plexiglass adhesive. After producing plexiglass parts we decided using aluminum tubes with 8mm diameter and 10mm tubes for T-shaped connection. However using alumınum for connections caused problems due to the wielding process of aluminum.
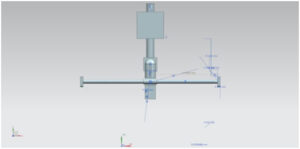
Moving Parts from the Top View
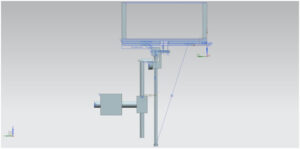
Moving Parts from Side View

Moving Parts from front View
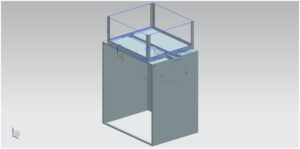
Assembly of the System