TEAM MEMBERS
Seymen EKİNCİ
H. İbrahim ÖNAL

A sewing machine is a textile machine used to stitch fabric, cards and other material together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. Since the invention of the first working sewing machine, generally considered to have been the work of Englishman Thomas Saint in 1790, the sewing machine has vastly improved the efficiency and productivity of fabric, clothing and needle industries.
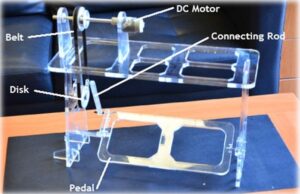
Today, there are sewing machines with electric motors but the manual ones include a four bar mechanism that converts pedal’s motion to a continous motion for the needle. Basically by foot, the pedal gains a rotational motion between 70-80 degrees.
In our project, we built a manual sewing machine and tried to move pedal by a servo motor but couldn’t succeed. Because the pedal’s motion should be with specified velocity and acceleration in order to gain fully continous rotation for pulley at upside. Therefore we give a continous rotation to pulleyat top and monitored the motion of the pedal.

As a main material for the body, we used laser-cut plexiglass parts. Two same diametered pulleys with a belt are used to transmit the power from the motor to the pedal. One pulley is directly connected to the DC motor standing upside. Pedal and pulley at bottom are connected via a connecting rod.
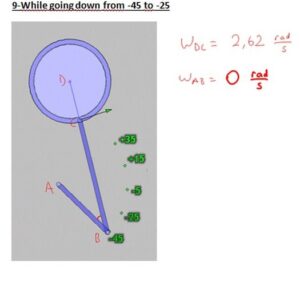
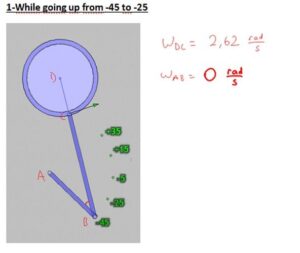
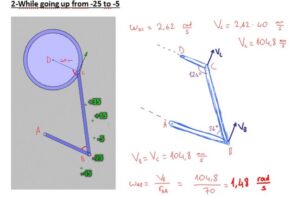
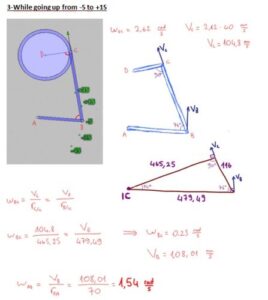
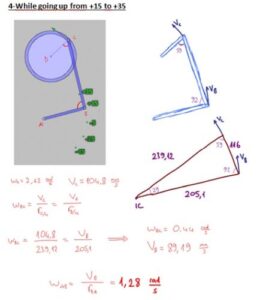
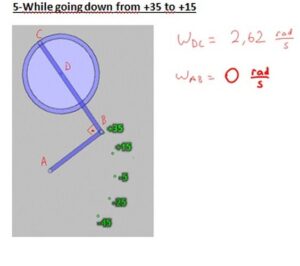
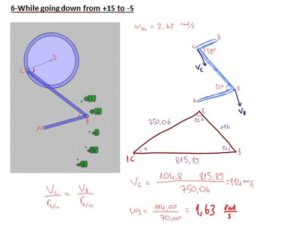
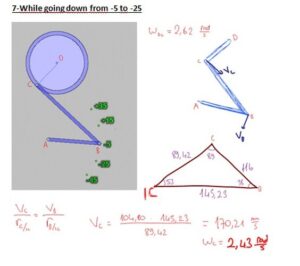
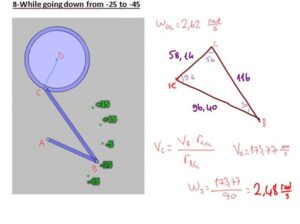
In our project, we have a system that converts the continous rotation (360°)to a rotation that goes only 80°. Our pedal goes form -35° to +45° rotational motion with varying angular velocity and angular acceleration. Because the angular speed is varying, here is the way we use to compare the calculated values with real values gathered from the machine;
– We seperated the way pedal follows into 20°parts.
-Then, we made calculations for every cases in which the pedal goes +35°, +15°, -5°,-25°,-45°.
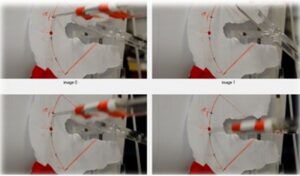
To get the real angular velocity values of the pedal on those angle values, we recorded a high quality video and found how much time takes for the pedal to follow those seperated ways.
At the end, calculated angular velocity values are converted to the time periodsthat the pedal takes between those seperated 20° ways.
All results from machine and calculations are compared at the end. Additional to this, you can see the simulation