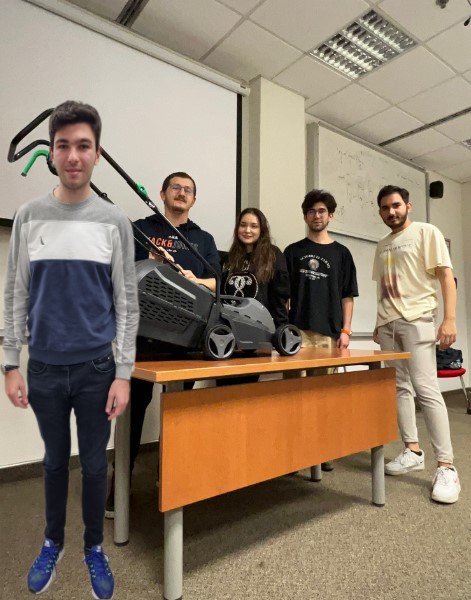

CAN KUT
BERK KAYTANCI
BEGÜM TÜRKEL
RECEP EMİR KOÇ
MEHMET TANHAN TOYGAR
Introduction
– A lawn mower is a device that cuts grass.
– The lawn mower’s operating concept is to rotate the blades at a high speed, which helps cut the grass by generating kinetic energy.
– The blade, which is connected to the Electric motor controlled by a pin in the handle, rotates and cuts the grass.

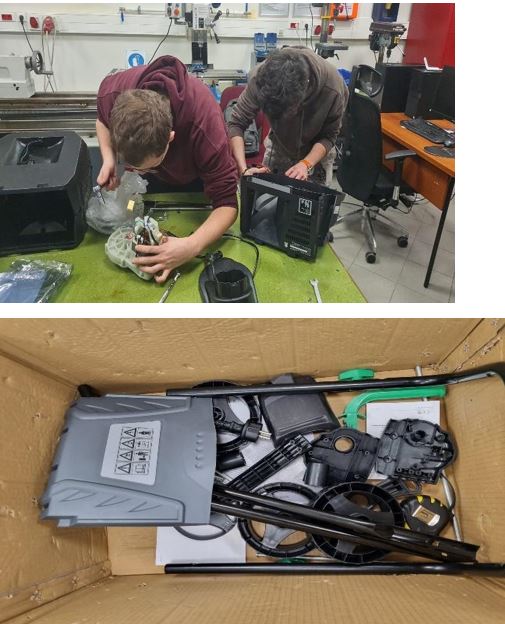
Disassembly
We measured the dimensions of the pieces using calipers. Doing precise measurements was difficult as some parts were larger than the size that could be measured with a caliper. Since some of the parts were combined with heat treatment, we could not separate them and we had to draw them as one piece. By plotting the dimensions of the parts to fit the parts they need to be joined, we found the lengths we couldn’t measure.

Exploded View
– Our object has 59 separate parts.
– Our assembly file contains 42 parts.
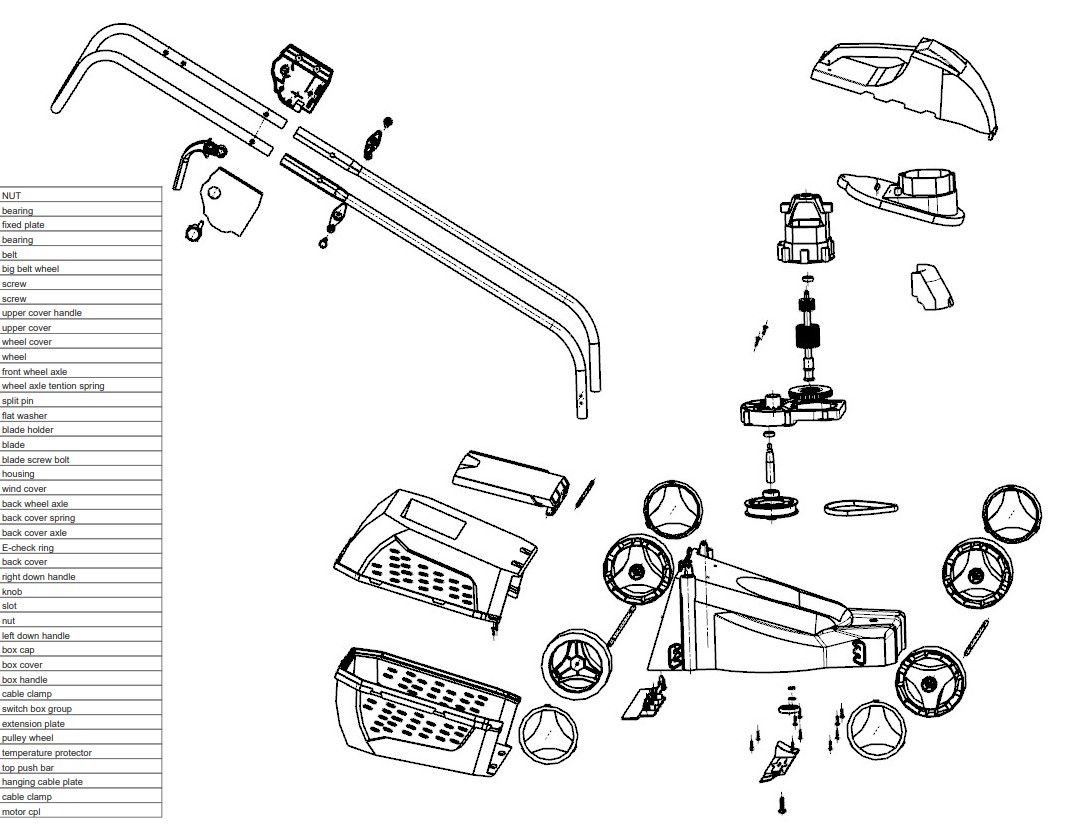
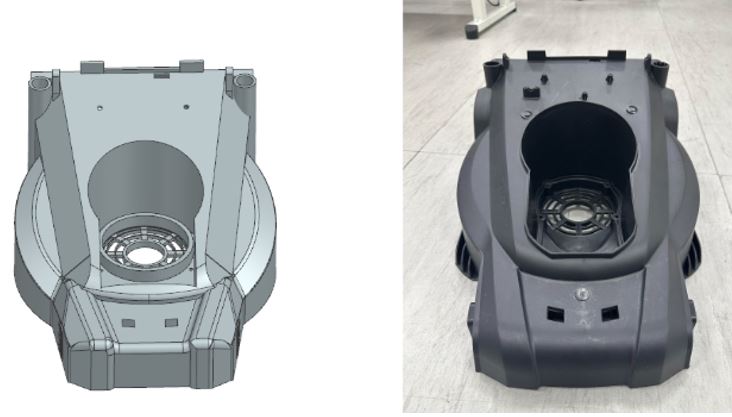
Part Comparisons and NX Commands

Drafting and Tolerances
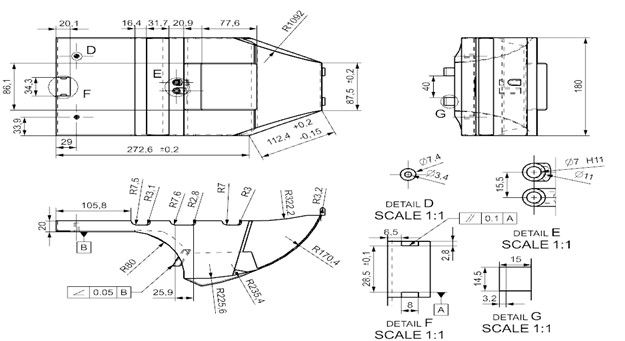
I gave the angularity tolerance according to the hole extension where the handle will enter and point B located on the bottom base because the other end of the handle should touch the B surface. I also gave the parallelism tolerance between the two gaps, which the handle should enter at the bottom. If these two gaps are not parallel enough, the tip of the handle cannot fit there.
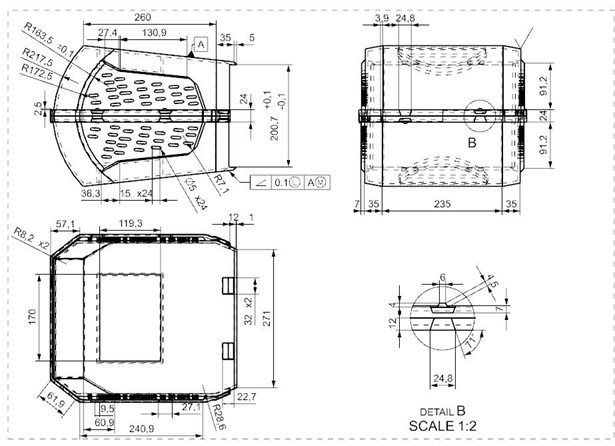
This is the drafting of box cover. I used the angularity tolerance which is control the orientations of features to one another. In the text book which we cover states that Angularity specifies the condition of a surface or features axis at a spesified angle from a datum plane or datum axis. In this draft I put angularity tolerances between the upper and lower surface of box cover. And I also used datum features as reference to control other features on the box cover. Then I also put biletarel tolerances which lengths are not an integer and important part of my draft. Also I put the surface finish symbol which is the check mark with its point resting on the surface.